| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
References
|
| |
|
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
|
|
| |
|
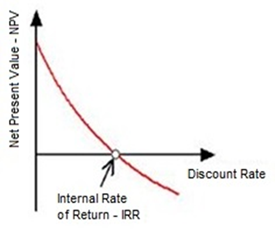
IRR is the discount
rate that makes the NPV (net present value) equal to zero; IRR is also called
effective interest rate, or rate of return. It is used to evaluate an
investment or project. Typically the higher the IRR, there is more
possibility to undertake the project.
|
|
| |
|
IRR is a rate, a
percentage, while NPV is an absolute value. IRR is usually used to calculate
the profitability of an investment or a project. If the IRR is greater than
the cost of capital, the investment or project may be accepted. Otherwise, it
should be rejected.
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
How to calculate IRR?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
NPV formula is as below:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
NPV =
|
Ʃ
|
|
Ct
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
(1+i)ᵗ
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
t=0
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Since IRR is the rate to make NPV=0, we get the
below functions:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ʃ
|
|
Ct
|
= 0
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
(1+i)ᵗ
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
t=0
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
or
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
PV of benefits - PV of
costs = 0
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
“i” is IRR, as the only unknown,
it can be solved by using numerical or graphical analysis techniques.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Let's see the example:
|
|
| |
|
An $85,000
investment returned $30,000 per year over a 5-year lifespan, what is the rate
of return on the investment?
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Solution:
|
|
| |
|
30000/(1+i) +
30000/(1+i)² + 30000/(1+i)³ + 30000/(1+i)⁴ + 30000/(1+i)⁵ = 85000
|
|
| |
|
IRR is 22.5%.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|